Index




Membership





Volume: 31 Issue: 3 - 2021
| 1. | Cover Page I (300 accesses) |
| 2. | Advisory Board Pages II - IV (363 accesses) |
| 3. | Publication Policies and Writing Guide Pages V - VIII (217 accesses) |
| 4. | Contents Pages IX - X (304 accesses) |
| REVIEW | |
| 5. | Screening of Diabetes in Pregnancy Barış Sever, Halil Gursoy Pala doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.60420 Pages 293 - 300 (444 accesses) The prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is approximately 6% of pregnant women in the United States. The prevalence ranges is about from 2% to 38% worldwide and varies among racial-ethnic groups, often paralleling the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. The prevalence also varies due to differences in screening practices, population characteristics (eg, mean age and body mass index [BMI] of pregnant women), testing method, and diagnostic criteria. The prevalence is increasing over time, possibly due to increases in mean maternal age and weight, particularly with increasing obesity. In 2010, the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups proposed new screening and diagnostic criteria for diabetes in pregnancy. Using these criteria, the global prevalence of hyperglycemia in pregnancy is estimated at 17%, with regional estimates ranging from 10% in North America to 25% in Southeast Asia. Different screening programs are carried out in different clinics, and all these differences lead to different results in the frequency of GDM. The criteria of the method and threshold value acceptance depends on the health policies of the countries, the experience of the clinicians and the characteristics of the patient population. In this review, we analyzed the methods recommended for GDM screening in pregnancy. |
| CLINICAL RESEARCH | |
| 6. | Evaluation of Trainings and Courses in Emergency Physicians Erhan Kaya, Ferdi Tanir doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.13281 Pages 301 - 305 (549 accesses) Amaç: Bu çalışmanın amacı, acil hekimlerinin gözüyle uzmanlık eğitimi ve hizmet içi kursların değerlendirilmesidir. Yöntem: Araştırma kesitseldir. Adana ili merkezinde acil servislerde çalışan 248 hekimden 202’sine 01 Temmuz-31 Aralık 2016 tarihleri arasında anket yapılmıştır. Ankette doktorların sosyodemografik bilgileri, sunulan uzmanlık eğitimi değerlendirmeleri, kurs alma durumları bulunmaktaydı. Tanımlayıcı analizler ve ki kare testi çalışmada kullanıldı. Bulgular: Çalışmamızda 30 yaş altında olan acil servis hekimi oranı %27,7, meslek hayatı 10 yıl altında olan hekim oranı ise %47 idi ve hekimlerin %20,8’i kurumunda acil tıp uzmanlık eğitimi aldığını belirtti. Uzmanlık eğitimi alan 42 hekimin %69’u eğitimin iyi olduğunu belirtti. Çalışmamızda hekimlerin %15,3’ü hizmet içi hiçbir kursa katılım göstermezken, %80,2’si kardiyopulmoner arrest vakalarında kendilerini yeterli görmektedir. Sonuç: Araştırmamızda acil servis hekimlerinde kardiyopulmoner resusitasyonla ilgili hizmet içi kurslara katılımın yüksek olduğu, ileri kardiyak yaşam desteği kursu alanların kardiyopulmoner arrest vakalarında kendini daha yeterli hissettiği saptanmıştır. Uzmanlık eğitimi yüksek oranda iyi düzeyde olarak değerlendirilmiştir. Objective: The aims of this research is to evaluate residency training and in-service courses through the eyes of emergency physicians. Method: This research is cross-sectional. A questionnaire was conducted with 202 of 248 physicians working in emergency departments in Adana city center between 01 July - 31 December 2016. The questionnaire included sociodemographic information of physicians, assessments of residency training offered, and taking courses. Descriptive analyzes and chi-square test were used in the study. Results: In our study, the rate of emergency physicians under the age of 30 was 27.7% and the rate of physicians with a career less than 10 years was 47% and 20,8% of the physicians stated that they received emergency medicine residency training in their institution. 69% of 42 physicians who received residency training stated that the training was good. In our study, 15.3% of the physicians did not participate in any course, while 80.2% of them considered themselves sufficient in cases of cardiopulmonary arrest. Conclusion: In our researh, it was found that the participation of the in-service courses related to cardiopulmonary resuscitation is high among emergency physicians. Those who take the advances cardiac life support course feel more sufficient in cases of cardiopulmonary arrest. Residency training has been evaluated as highly good. |
| 7. | The Variation of Pentraxin-3 in Febrile Patients Admitted With or Without Convulsions Şefika Bardak, Mine Cinbis, Yaşar Enli doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.88528 Pages 306 - 312 (607 accesses) Amaç: Febril konvülziyon çocukluk çağında en sık görülen konvülziyon tipidir. Pentraksin-3 uzun pentraksinler ailesine dâhil olan, yeni nesil bir akut faz reaktanıdır. Çalışmamızda birincil amacımız febril konvülziyon geçiren hasta grubu ile konvülziyon geçirmeyen ateş yüksekliği olan kontrol grubu arasında serum Pentraksin-3 düzeyi açısından farklılık olup olmadığının araştırılması idi. İkincil amacımız ise serum Pentraksin-3 düzeyinin klinikte daha sık kullanılan akut faz reaktanları (C-reaktif protein, beyaz küre sayısı) ile korelasyon gösterip göstermediğinin değerlendirilmesiydi. Yöntem: Çalışmamız Ocak 2014-Temmuz 2014 tarihleri arasında ileriye dönük olarak yürütüldü. Araştırmamıza bir üniversite hastanesi Çocuk Acil Polikliniği’ne getirilen 35 febril konvülziyonlu hasta (hasta grubu) ile yaş ve cinsiyet bakımından benzer, kronik hastalığı ve sürekli ilaç kullanımı olmayan, asıl yakınması ateş yüksekliği olan 35 hasta (kontrol grubu) dahil edildi. Çalışmaya alınan tüm olguların aktif yakınması, özgeçmiş ve soygeçmiş özelliklerini içeren anamnez bilgileri ile laboratuvar bulguları daha önce basılmış ve üzerinde hastanın yaş (ay olarak), cinsiyet gibi demografik bilgilerinin de bulunduğu formlara kaydedildi. İstatistiksel incelemede anlamlılık düzeyi ise p<0,05 olarak kabul edildi. Bulgular: Hasta ve kontrol grubu arasında yaş ve cinsiyet açısından istatistiksel olarak farklılık yoktu (p>0,05). Her iki grup arasında üre, kreatinin, elektrolitler, C-reaktif protein, beyaz küre sayısı değerleri açısından istatistiksel olarak anlamlı fark saptanmadı (p>0,05). Serum Pentraksin-3 düzeyi hasta grubunda ortalama 4,8±2,5 ng/ml, kontrol grubunda ise 4,1±2,3 ng/ml bulundu. İki grup arasındaki fark istatistiksel olarak anlamlı bulunmadı (p>0,05). Pentraksin-3 düzeyi ile C-reaktif protein düzeyi ve beyaz küre sayısı arasında istatistiksel olarak anlamlı ilişki saptanmadı. Sonuç: Bulgularımız serum Pentraksin-3 düzeyinin febril konvülziyon geçiren ve geçirmeyen ateşli hastalarda benzer olduğunu göstermektedir. Ayrıca Pentraksin-3’ün pratik uygulamalarda daha yaygın kullanılan akut faz reaktanları ile korelasyon göstermediği sonucuna varılmıştır. Objective: Febrile convulsions are the most frequent seizures in childhood. Pentraxin-3 is a new generation acute phase reactant that belongs to the family of long pentraxins. In our study, our primary aim was to investigate the difference in serum Pentraxin-3 levels between febrile convulsive patient group and non-convulsive fever control group. Our secondary aim was to evaluate the correlation between serum Pentraxin-3 levels and other more frequently used acute phase reactants (C-reactive protein, white blood cell count). Methods: Patients admitted to the pediatric emergency department between January 2014 and July 2014 were included in this prospective study The study included 35 febrile convulsive patients (patient group) and 35 non-convulsive febrile patients (control group) with similar age and gender, without chronic disease or ongoing medication brought to a university hospital Pediatric Emergency Department. Anamnesis information including active complaints, self and family history and laboratory findings of all cases included in the study were recorded on previously printed forms with demographic information such as age (month) and gender of the patient. In statistical analysis, the significance level was accepted as p <0,05. Results: There was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of age, gender, serum urea, creatinine, electrolytes, C-reactive protein and white blood cell counts (p>0,05). Serum Pentraxin-3 levels were 4,8±2,5 ng/ml in the patient group and 4.1±2.3 ng/ml in the control group. The difference between the two groups was not statistically significant (p>0,05). No correlation was found between Pentraxin-3 with C-reactive protein and white blood cell count. Conclusion: Our findings show that serum Pentraxine-3 levels are similar in patients with febrile convulsion and fever. In addition, it was concluded that Pentraxine-3 does not correlate with acute phase reactants, which are more commonly used. |
| 8. | The Assessment of HLA Sensitization Effect on Graft Function and Survival in Renal Transplant Recipients Derya Güleç, Tülay Kılıçaslan Ayna, Mustafa Soyöz, İsmail Sert, Cem Tuğmen, Aslı Özkızılcık Koçyiğit, Erhan Tatar, Adam Uslu, Zeki Soypaçacı, Burcu Çerçi, Murat Kılıçoğlu, İbrahim Pirim doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.70456 Pages 313 - 321 (480 accesses) Amaç: Anti-insan lökosit antikorları (HLA) greft sağkalımında özellikle de böbrek nakillerin önemli bir role sahiptir. Nakil öncesinde oluşan anti-HLA antikorları, özellikle donöre spesifik antikorlar, akut ve kronik rejeksiyona sebep olabilir. Bu çalışmada, böbrek nakli olmuş hastalarda nakil öncesinde bulunan anti-HLA antikorlarının greft fonksiyonu, kaybı ve hasta sağkalımı üzerindeki etkilerinin değerlendirilmesi amaçlanmıştır. Yöntem: PRA (panel reaktif antikor) seviyeleri Luminex ve Flow sitometri gibi boncuğa dayalı yöntemlerle izlenmiştir. Hastaların nakil sonrası glomerular filtrasyon oranları (GFR) ve birinci, üçüncü ve beşinci yıllardaki greft kayıplarıyla hasta sağkalımları istatistiksel olarak değerlendirilmiştir. Bulgular: Bu çalışma, akrabadan nakil olan hastaların daha düşük anti-HLA antikor seviyelerine ve daha yüksek eGFR değerlerine sahip olduklarını göstermiştir. Akut rejeksiyon atağı (ARE) geçirmiş hastalar geçirmemiş hastalara göre daha düşük eGFR değerlerine sahiptir. Beş yıllık greft sağkalımı incelendiğinde, anti-HLA Sınıf I/II pozitif hastalarda ve negatif hastalarda sırasıyla %65.6±9.8 ve %86.5±3.2%, ARE pozitif ve negatif hastalarda ise sırasıyla %74.8±6.4% ve %84.3±2.6 olarak bulunmuştur. Greft ve hasta sağkalımı cox regresyon testiyle analiz edildiğinde, eGFR değerinin greft kaybının göstergesi olduğu belirlenmiştir (HR=0.843, p=0.00). Sonuç: Bu çalışmada, anti-HLA antikor karakterizasyonuyla greft sağkalımı arasında istatistiksel olarak anlamlı bir korelasyon bulunmamasına rağmen, anti-HLA sınıf I/II pozitifliği olan bütün hastalar ile ARE pozitif hastalarda en kısa greft sağkalımı gözlenmiştir. Nakil öncesinde ve sonrasında PRA testlerinin periyodik olarak yapılmasının önemi ve gerekliliği devam etmektedir. Objective: Anti-human leukocyte antibodies (HLA) play an important role in graft survival, particularly in kidney transplantation. Preformed anti-HLA antibodies, especially donor specific antibodies can cause acute and chronic rejections. In this study, it was aimed to assess the effects of anti-HLA antibodies in kidney patients before transplant on graft function, failure, and patient survival. Methods: PRA (Panel Reactive Antibody) levels were monitored using bead based methods such as Luminex and flow cytometry. Post-transplant estimated glomerular filtration ratios (eGFR) among first, third, and fifth year patient survivals and graft failures were statistically analyzed. Results: In this study, it was observed that related transplants had low levels of PRAs, and their eGFRs were at normal reference range. The patients without acute rejection episode (ARE) had higher eGFR values than those with ARE. When five year-graft survival terms were evaluated, it was found that 65.6±9.8% and 86.5±3.2% graft survival terms were detected in anti-HLA Class I/II positive and negative patients, whereas 74.8±6.4% and 84.3 ±2.6% graft survival terms were observed in ARE positive and negative patients, respectively. eGFR value is a predictor of graft failure and patient survival. Our Cox regression analyses (HR=0.843, p=0.00) also supported this information. Conclusion: The study concluded that although the correlation between PRA positivity and graft survival were not significant, the shortest graft survival was observed in PRA positive patients in the whole cohort and ARE positive patients. The importance and requirement of pre- and post-transplant PRA tests continue. |
| 9. | Evaluation of Sociodemographic Characteristics and Depression Diagnosis of Adolescents who Had Suicide Attempt Ayşe Nihal Eraslan, Rezzan Aydın Görücü, Mehmet Öztürk, Arzu Yılmaz, Medine Ayşin Taşar doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.79282 Pages 322 - 332 (1049 accesses) Amaç: Ergenlerdeki intihar girişimleri, acil servise yapılan psikiyatrik başvurular arasında en yaygın başvuru sebeplerinden biri haline gelmiştir. Bu çalışmayla ergenlik dönemi özellikleri de göz önünde bulundurularak intihar girişiminde bulunan ergenlerin sosyodemografik ve klinik özelliklerinin belirlenmesi, eşlik eden depresyon tanısının saptanması ve risk faktörlerinin değerlendirilmesi amaçlanmıştır. Yöntem: Araştırmaya Nisan 2018-Aralık 2018 tarihleri arasında Ankara Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi Çocuk Acil Bölümü’ne intihar girişimi nedeni başvurmuş ve Çocuk Ergen Ruh Sağlığı Hastalıkları Bölümü’ne yönlendirilmiş hastalar alınmıştır. Araştırma kapsamında “Çocuklar İçin Depresyon Ölçeği”, “Beck Depresyon Ölçeği” ve “Sosyodemografik Veri Formu” kullanılmıştır. Hastaların psikiyatrik muayene sonucunda DSM-5’e göre “Major Depresyon Bozukluğu” tanısı alıp almadığı da değerlendirilmiştir. Analizlerde SPSS 24.0 kullanılmıştır. T Testi, Kruskal Wallis Testi, ki-kare ve Fisher’s exact test uygun yerlerde kullanılmıştır. Bulgular: İntihar girişiminde bulunan toplam 38 olgunun %92,1’ini (n=35) kızlar oluşturmaktaydı. Olguların %92,1’inin (n=35) ilaç içerek intihar girişiminde bulundukları saptandı. Olguların yaklaşık yarısı (%44,7 n=17) intihar sebebini “ailevi stresörler” olarak belirtti. Psikiyatrik değerlendirme sonucunda olguların %42,1’inde (n=16) DSM-5’e göre “Major Depresyon Bozukluğu” tanısı saptandı. Sonuç: İntihar girişiminde bulunan ergenlerdeki bireysel ve çevresel etkenlerin kapsamlı olarak değerlendirilmesinin risk faktörlerinin anlaşılmasında önemli olduğu düşünülmüştür. Gençlerin sorunlarla başa çıkma becerilerinin artırılmasına, gençlere problem çözme becerilerinin kazandırılmasına ve ailelerin ergen bireylere yaklaşım konusunda bilgilendirilmesine yönelik profesyonel psikososyal destek sistemlerinin güçlendirilmesinin koruyucu önlemlere katkı sağlayabileceği düşünülmüştür. Objective: Suicide attempts of adolescents have become one of the most common reasons among the admission to emergency departments for psychiatric reasons. The aim of this study is to identify sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, the diagnosis of depressive disorder and to assess the risk factors of adolescents who attempted suiside. Method: For this study, the patients that were admitted to Ankara Research and Training Hospital Emergency Department and were referred to Child and Adolescent Psychiatry outpatient clinic due to suicide attempt between April 2018 and December 2018 were included. “Child Depression Inventory”, “Beck Depression Inventory “ and “Sociodemographic Data Form” were used for the study. It was also evaluated whether the patients were diagnosed with “Major Depressive Disorder” according to DSM-5 as a result of psychiatric examination. SPSS 24.0 was used in the analyzes. T-test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Chi-square and Fisher’s exact test were used where appropriate. Results: Out of 38 patients who attempted suicide, 92,1% (n=35) were female. It was found that 92.1% (n=35) of the cases attempted suicide by overdose drug intake. Approximately half of the cases (44.7% n=17) reported the reason for suicide as “familial stressors”. As a result of the psychiatric evaluation, 42.1% (n=16) of the cases were diagnosed with “Major Depressive Disorder” according to DSM-5. Conclusion: Comprehensive evaluation of individual and environmental factors in adolescents who attempted suicide is considered important to identify the risk factors. Moreover strengthening the professional psychosocial support systems about increasing coping skills, gaining problem-solving skills of adolescents and informing families about approach to adolescents are thought that may contribute to protective measures. |
| 10. | Urinary Tract Anomalies in Children With Congenital Heart Disease Detected During the Procedure of Cardiac Catheterization Çağla Çağlı, Sevcan Erdem, Bahriye Atmış, Aysun Karabay Bayazit, Fadli Demir, Hüsnü Demir, Nazan Özbarlas doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.26986 Pages 333 - 337 (496 accesses) Amaç: Çocukluk çağında konjenital kalp hastalıkları morbidite ve mortalitenin önemli bir nedenidir. Konjenital kalp hastalığı olan çocuklarda kardiyak olmayan anomalilerin sıklığı %7-50 arasındadır. Üriner sistem anomalileri konjenital kalp hastalığı olan çocuklarda önemli bir risk faktörüdür. Bu çalışmanın amacı, konjenital kalp hastalığı olan çocuklarda kardiyak kateterizasyon sırasında tespit edilen üriner sistem anomalilerinin varlığını, tiplerini ve sıklığını değerlendirmektir. Yöntem: Konjenital kalp hastalıkları nedeniyle kardiyak kateterizasyon uygulanan 6000 hastanın sineurografi kayıtları retrospektif olarak analiz edildi. Saptanan üriner sistem anomalileri renal agenezi, renal ektopi, renal füzyon, displastik böbrek, obstrüktif üropati, vezikoüreteral reflü, üreter anomalisi ve mesane anomalisi olarak incelendi. Hastalar sağ ventrikül çıkış yolu tıkanıklığı, sol ventrikül çıkış yolu tıkanıklığı, soldan sağa şant kalp hastalığı ve siyanotik veya kompleks kalp hastalığı olarak gruplandırıldı. Gruplar üriner sistem anomalisi tipleri açısından karşılaştırıldı. Bulgular: Üriner sistem anormallikleri olan toplam 76 hasta (47 erkek ve 29 kız) tespit edildi. Tespit edilen üriner sistem anomalilerinin dağılımı 43 (%56,5) hastada obstrüktif üropati, 14 (%18,4) hastada renal agenezi, 14 (%18,4) hastada üreter anomalisi, 3 (%3,9) hastada renal füzyon, 1 (%1,3) hastada renal ektopi, 1 (%1,3) hastada vezikoüreteral reflü şeklinde idi. Konjenital kalp hastalıklarına göre gruplara ayrılan hastalarda arasında üriner sistem anomali tipleri açısından anlamlı bir fark tespit edilmedi (p>0,05). Sonuç: Konjenital kalp hastalığı olan çocuklarda, üriner sistem anomalilerinin de eşlik edebileceği unutulmamalı, bu nedenle kalp kateterizasyonu sırasında üriner sistem de değerlendirilmelidir. Objective: Congenital heart diseases in childhood are an important cause of morbidity and mortality. The frequency of non-cardiac anomalies in children with congenital heart diseases is between 7-50%. Urinary system anomalies are an important risk factor in children with congenital heart diseases. The aim of this study was to evaluate the presence, types and frequency of urinary system anomalies detected during cardiac catheterization in children with congenital heart diseases. Methods: The cineurography records of 6000 patients who underwent cardiac catheterization due to congenital heart diseases were retrospectively analyzed. Urinary system anomalies detected were examined as renal agenesis, renal ectopia, renal fusion, dysplastic kidney, obstructive uropathy, vesicoureteral reflux, ureter anomaly and bladder anomaly. Patients were grouped as right ventricular outflow tract obstruction, left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, left-to-right shunted hearth disease and, cyanotic or complex heart diseases. The groups were compared in terms of urinary system anomaly types. Results: Seventy-six patients (47 male and 29 female) with urinary system abnormalities were detected. Obstructive uropathy was found in 43 (56.5%) patients, renal agenesis was found in 14 (18.4%) patients, ureter anomaly was found in 14 (18.4%) patients, renal fusion was found in 3 (3.9%) patients, renal ectopia was found 1 (1.3%) patient, vesicoureteral reflux was found in 1 (1.3%) patient. There was no significant difference in term of the urinary system anomaly types among the groups (p>0.05) Conclusion: Urinary system anomalies may also be frequently accompanied in children with congenital heart diseases, so urinary system should also be evaluated during the cardiac catheterization procedure. |
| 11. | Choroidal Thickness in Children with Congenital Heart Disease Measured by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Fatos Alkan, Semra Sen, Ercument Cavdar, Senol Coskun doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.66587 Pages 338 - 343 (379 accesses) Amaç: Spektral-domain optik koherens tomografi (SDOKT) kullanarak doğuştan kalp hastalıklı (DKH) çocuklarda koroid kalınlığının değerlendirilmesi amaçlanmıştır. Doğuştan kalp hastalığında komplikasyonların başlıca nedeni, siyanoz için tipik olan düşük arteriyel oksijen saturasyonu ve polisitemidir. Bu parametreler retinal hasarı artırabilir, çünkü hemodinamik regülasyon makuler alt alanların yapısal ve işlevsel bütünlüğü için gereklidir. Yöntem: Bu prospektif çalışmada 30 DKH’lı ve 30 sağlıklı çocuk karşılaştırıldı. Koroid kalınlığı SDOKT ile incelendi (Retinascan RS-3000; Nidek). Koroidal kalınlık; subfovea, 500 μm ve 1000 μm nazal fovea (N500, N1000) ve 500 μm ve 1000 μm temporal foveal alan (T500, T1000) ölçülerek elde edildi. Gruplar arasındaki istatistiksel karşılaştırmalar için sadece sağ göz değerleri kullanıldı. Kardiyak patolojiler fizyolojik olarak volüm yükü yapan ve siyanotik olarak iki kategoriye ayrıldı. Bulgular: DKH’li çocuklarda yaş ortalaması 11.0±3.5 yıl, kontrol grubunda 10.9±3.6 yıl idi (p = 0.971). DKH’li çocuklar, sağlıklı kontrollerle karşılaştırıldığında istatistiksel olarak anlamlı koroidal kalınlık ölçümleri saptanmadı (p>0.05). Sonuç: DKH çocuklar da yüksek hematokrit, düşük arteriyel oksijen saturasyonu veya aşırı volüm yükü nedeniyle olası retinal vasküler değişikler beklenmesine karşın, çalışmamızda DKH’lı hastaların normal koroidal kalınlık gösterdiklerini saptadık. Bu durum hastalarımızın çoğunda uygulanmış medikal yada cerrahi tedavi ile retinal vasküler değişiklerin iyileştirilmesine bağlı olabilir. Objective: The main reason for complications in congenital heart diseases (CHD) is decreased blood oxygen saturation and polycythemia which are typical for cyanosis. These parameters may promote the damage of the retina because haemodynamic regulation is essential for the structural and functional integrity of the macular subfields. The aim of this study was to evaluate choroidal thickness (CT) measurements in children with CHD using spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT). Methods: This prospective study compared 30 CHD and 30 healthy control children. CT was examined with spectralis spectral-domain OCT (Retinascan RS-3000; Nidek). CT was obtained at the subfovea, 500 μm and 1000 μm nasal to the fovea (N500, N1000) and 500 μm and 1000 μm temporal to the fovea (T500, T1000). Only the right eye values were used for statistical comparisons between the groups. The domain cardiac lesions were divided physiologically into two categories: volume overload and cyanotic. Results: Mean age was 11.0±3.5 years in CHD childrens and 10.9±3.6 years in the control group (p=0.971). Children with CHD had no statistically significant CT measurements compared with healthy controls (p>0.05). Conclusion: Although in high haematocrit, low oxygen saturation or the presence of the volume overload in the history of CHD patients, our data suggests that patients with CHD show normal CT. The reason may be medical and surgical treatment of hypoxia, erythrocytosis and volume overload in CHD patients. |
| 12. | The Impact of Chemotherapy on the EORTC QLQ-C30 and LC-13 Quality of Life Scales in Patients with Lung Cancer Muge Guvencli, Enver Yalniz, Berna Komurcuoglu, Ahmet Emin Erbaycu, Gamze Karakurt doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.73626 Pages 344 - 354 (457 accesses) Amaç: Akciğer kanseri hastalarında yaşam kalitesi kavramı; fiziksel, psikolojik ve sosyal olmak üzere pek çok komponenti içermektedir. Bu çalışmada akciğer kanserli hastalarda kemoterapinin yaşam kalitesi üzerine etkisinin yaşam kalitesi ölçekleri kullanılarak belirlenmesi amaçlanmıştır. Yöntem: Araştırmaya yeni tanı alan ve kemoterapi planlanan 50 inoperabl akciğer kanserli hasta alındı. Hastalar tedaviye yanıt ve toksisite yönünden izleme alındı. EORTC QLQ-C30 ve LC13 ölçeklerinin Türkçe sürümleri her siklus öncesi uygulandı. Bulgular: Yaş ortalaması 60.1 yıldı. Yaş ve gelir düzeyi ile yaşam kalitesi parametreleri arasında fark bulunmadı. Erkeklerin; fiziksel, sosyal ve uğraş fonksiyonlarının ve genel sağlık durumu değerlendirmesi kadınlara göre daha iyi idi. Komorbiditesi olmayanların, 1. Siklus KT’de genel sağlık durumu değerlendirmesi daha iyi idi. Kemoterapi ile sosyal fonksiyonlarda, ekonomik durumda kötüleşme, nöropati, kabızlık ve saç dökülmesinde artış saptandı. Tedaviye tam veya kısmi yanıt elde edilen hastaların, fiziksel, uğraş, duygusal, kavrama, sosyal fonksiyonlarının, ekonomik durumlarının ve genel durum değerlendirmesinin daha iyi olduğu, yorgunluk, ağrı, nefes darlığı, nöropatinin daha az olduğu ve iştahın daha iyi olduğu belirlendi. Toksisitelerin QLQ C30 ve LC13 ölçeklerini olumsuz yönde etkilediği görüldü. Sonuç: Akciğer kanserinde komorbidite varlığı, düşük eğitim düzeyi, sosyoekonomik durum ve kemoterapiye bağlı hematolojik/gastrointestinal toksisiteler yaşam kalitesini etkileyen en önemli parametrelerdir. Kemoterapi ile sosyal fonksiyonlar ve ekonomik parametrelerde kötüleşme ile birlikte yan etkilerde artış izlenmiştir. Radyolojik tam veya kısmi yanıt, küçük hücreli karsinom hücre tipi kemoterapi ile yaşam kalitesi parametrelerinin olumlu etkilendiği durumlardır. Objective: The concept of quality of life (QoL) in lung cancer includes many physical, psychological and social components. We aimed to assess the effect of chemotherapy (CT) on QoL of lung cancer patients using QoL scales. Methods: Fifty inoperable lung cancer patients who were newly diagnosed and taken into a CT plan were included. Patients were followed in terms of responsiveness and toxicity. Turkish versions of the EORTC QLQ-C30 and LC13 scales were used before every cycles. Results: The average age was 60.1 years. There was no difference between QoL and age/income levels. The assessment of physical, social and occupational functions and overall health status of the male patients was better than female. Overall health status without comorbidity was better in the first cycle CT. Chemotherapy led to deterioration in social functions and economic status together with increase in neuropathy, constipation and hair loss. Patients with complete or partial response to treatment were observed to have better physical, occupational, emotional, cognitive and social functions, economic status and overall health; less fatigue, pain, shortness of breath, neuropathy and better appetite. Toxicities were found to affect the QLQ C30 and LC13 scales adversely. Conclusion: Presence of comorbidity, low education levels, socioeconomic status and CT induced hematologic/gastrointestinal toxicities are the major parameters affect QOL in lung cancer. Chemotherapy leads to deterioration in social functions, increase in adverse events as well as worsening in economic status. Radiologic complete or partial response and small cell carcinoma are states in which parameters of QoL are affected positively by chemotherapy. |
| 13. | The Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic on Pain, Physical Activity, and Anxiety in Individuals with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain Gülşah Özsoy, Hayriye Yilmaz, Ismail Ozsoy doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.23356 Pages 355 - 361 (444 accesses) Amaç: COVID-19 pandemisi, kronik ağrıyı potansiyel olarak tetikleyebilecek ve artırabilecek birçok özelliğe sahiptir. Bu çalışmanın amacı, kronik kas-iskelet sistemi ağrısı olan bireylerde pandeminin hem izolasyon hem de kontrollü sosyal yaşam dönemlerinde ağrı, fiziksel aktivite ve anksiyete üzerindeki etkisini incelemekti. Yöntem: Çalışmaya kronik kas-iskelet sistemi ağrısı olan 71 kişi dahil edildi. Üç farklı dönem (pandemi öncesi, izolasyon ve kontrollü sosyal yaşam) değerlendirildi ve analiz edildi. Ağrı şiddeti (Görsel Analog Skala (VAS)), koronavirüs anksiyetesi (Koronavirüs Anksiyete Ölçeği Kısa Formu (CAS-SF)) ve fiziksel aktivite düzeyi (Uluslararası Fiziksel Aktivite Anketi Kısa Formu (IPAQ-SF)) değerlendirildi. Bulgular: VAS istirahat skoru izolasyon döneminde anlamlı olarak COVID-19 öncesine göre yüksekti (p=0.002). VAS aktivite skoru izolasyon döneminde anlamlı olarak COVID-19 öncesine (p<0.001) ve kontrollü sosyal hayat dönemine (p<0.001) göre yüksekti. Katılımcıların en düşük IPAQ-SF skoru (p<0.001) ve en uzun oturma süresi (p<0.001) izolasyon dönemindeydi. Katılımcıların CAS-SF skoru izolasyon döneminde anlamlı olarak kontrollü sosyal hayat dönemine göre yüksekti (p<0.001). Sonuç: COVID-19 pandemisi sürecinde izolasyon dönemindeki alınan önlemler kronik muskuloskeletal ağrılı bireylerde ağrı şiddeti, fiziksel aktivite ve anksiyetenin olumsuz etkilenmesine neden olurken kontrollü sosyal hayat dönemi ile birlikte ağrı şiddeti ve anksiyete düzeyinde azalma ve fiziksel aktivitede artış olmuştur. Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic has many features that can potentially trigger and increase chronic pain. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of the pandemic on pain, physical activity and anxiety in individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain, in both periods of isolation and controlled social life. Methods: Seventy one individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain were included in the study. Three different periods (pre-pandemic, isolation and controlled social life) were evaluated and analyzed. Pain intensity (Visual Analogue Scale (VAS)), coronavirus anxiety (Coronavirus Anxiety Scale Short Form (CAS-SF)), and physical activity level (International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF)) were evaluated. Results: The VAS resting score was significantly higher during the isolation compared to the pre-pandemic period (p = 0.002). The VAS activity score was significantly higher in the isolation period compared to both pre-pandemic (p <0.001) and controlled social life periods (p <0.001). The lowest IPAQ-SF score (p <0.001) and the longest sitting time (p <0.001) were in the isolation period. The CAS-SF scores were significantly higher in the isolation period compared to the controlled social life period (p <0.001). Conclusion: While the measures taken during the isolation period had negative impacts on the severity of pain, physical activity and anxiety levels in individuals with chronic musculoskeletal pain, gradual deconfinement in the controlled social life period led to a decrease in pain intensity and anxiety and an increase in physical activity. |
| 14. | Can Preoperative Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio Predict Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome That Develops After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy? Uygar Miçooğulları, Orcun Celik, Mehmet Çağlar Çakıcı, Erdem Kisa, Cem Yucel, Okan Nabi Yalbuzdag, Mehmet Yoldaş, Hakan Üçok, Tufan Süelözgen, Mehmet Zeynel Keskin, Yusuf Özlem İlbey doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.38980 Pages 362 - 367 (500 accesses) Objective: First objective of this study was to find out factors influencing development of postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) after percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL). Secondary objective was to point out the role of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in SIRS estimation. Method: The data of 756 patients that underwent PNL for kidney stones between 2012 and 2019 were evaluated retrospectively. Patients were divided into 2 groups as non-SIRS and SIRS group. The effects of NLR, PLR and other operative and demographic variables on development of SIRS were investigated. Multivariate logistic regression analysis that was performed on variables that were significant in the univariate analyses was used to establish independent risk factor for post-PNL SIRS. Results: Univariate analysis revealed a significant association between presence of SIRS and preoperative PLR (p<0.001), preoperative NLR (p<0.001), blood transfusion (p<0.001), stone volume (p=0.03), staghorn stone (p<0.001), and preoperative creatinine levels (<0.001). Multivariate logistic regression analyses of these risk factors showed that NLR (p<0.001), PLR (p<0.001), and blood transfusions (p<0.001) were independently associated with SIRS. When the cut-off value of PLR was 120.5, the development of SIRS was predicted with 80.1% specificity and 81% sensitivity. When the cut-off value of NLR was 2.75, the development of SIRS was predicted with 64% specificity and 63.7% sensitivity. Conclusion: Preoperative PLR and NLR are effective and inexpensive biomarkers that can be used to predict SIRS and sepsis after PNL. We recommend that patients with PLR >120.5, NLR >2.75, and blood transfusions should be monitored closely due to the possible development of serious complications. |
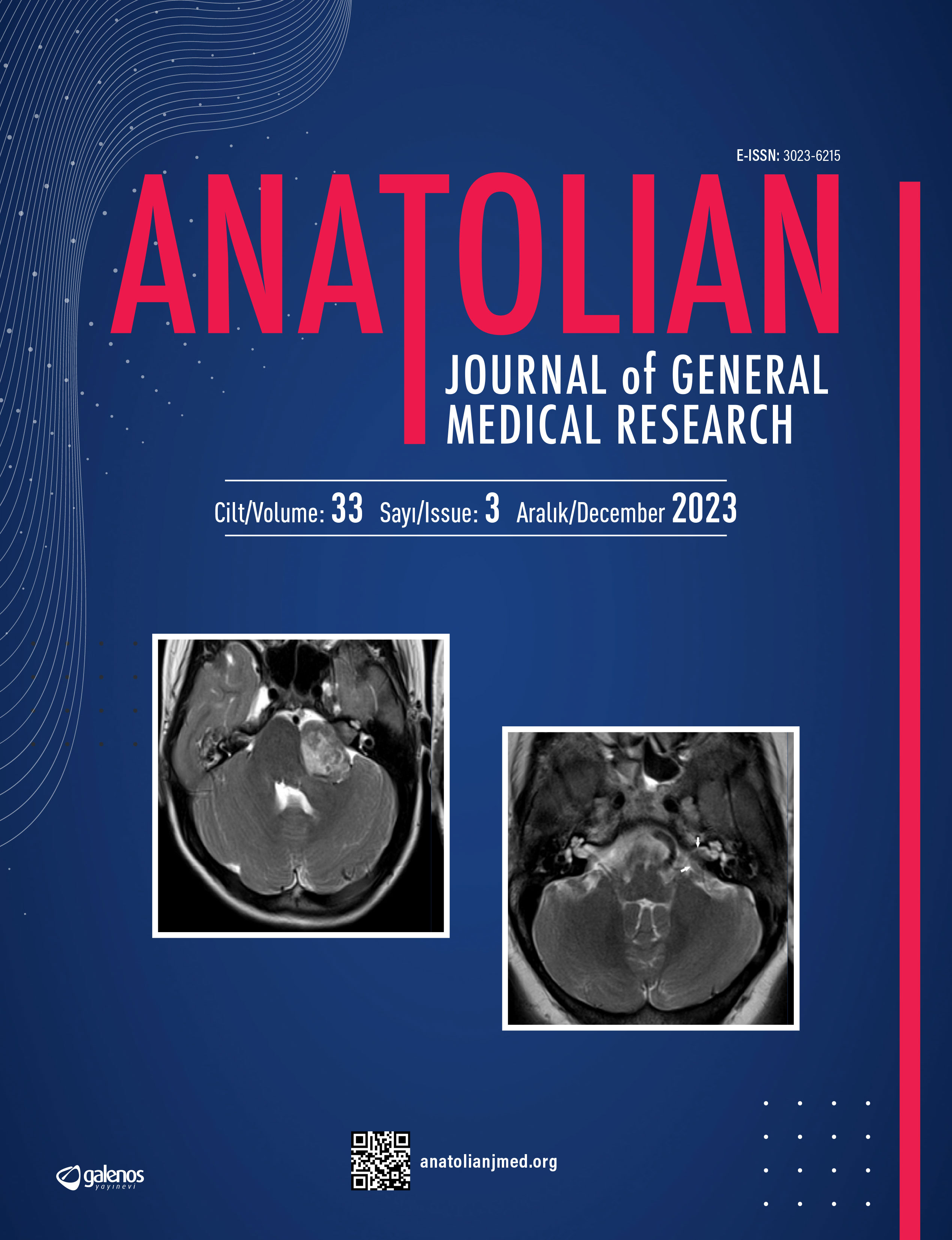
| 15. | Evaluation the Frequency of Cerebral Arterial Fenestrations and Their Association with Cerebral Aneurysm by CT Angiography Rıdvan Pekçevik, Yeliz Pekcevik doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.69672 Pages 368 - 373 (1248 accesses) Amaç: Fenestrasyonlar ortak bir orijinden kaynaklanan, daha sonra iki paralel lümene ayrılan ve distalde tekrar birleşen vasküler varyasyonlardır. Biz çalışmamızda serebral arteriyel fenestrasyonların sıklığının ve serebral anevrizma ile ilişkisinin bilgisayarlı tomografi (BT) anjiografi ile değerlendirilmesini amaçladık. Yöntem: Ocak 2017- Aralık 2020 arasında hastanemizde serebral BT anjiografi incelemesi yapılan, 18 yaş ve üzeri, bilinen vasküler bir hastalığı olmayan, daha önce cerrahi ya da girişimsel tedavi olmamış hastaların serebral BT anjiografi incelemesi retrospektif olarak değerlendirilmiştir. Fenestrasyon lokalizasyonu ve anevrizmalar not edilmiştir. Bulgular: BT anjiografisi olan 887 (ortalama yaş 54.8 yıl, yaş aralığı 18-63; 405 kadın ve 482 erkek) hasta değerlendirildi. 152 hastada 164 fenestrasyon saptanmış olup fenestrasyon sıklığı %17.1 bulundu. Fenestrasyonların en sık görüldüğü lokalizasyon, anterior kommunikan arter olup (%51.2), bunu vertebrobaziler sistem fenestrasyonları (%28.7) takip etmekteydi. Çalışmamızda lokalizasyondan bağımsız olarak, fenestrasyon ile anevrizma arasında anlamlı bir ilişki saptanmamıştır (p>0.05). Ancak fenestrasyon ve anevrizma birlikteliğinde, bu ikisi aynı lokalizasyonda daha sık görülmektedir (p: 0.005). Sonuç: Fenestrasyon nadir olmayan bir varyasyondur. En sık anterior kommunikan arter ve vertebro-baziler sistemde görülmektedir. Serebral arter fenestrasyonları aynı lokalizasyonda yer alan anevrizma ile ilişkili olabilir. Fenestrasyon saptandığında eşlik eden anevrizma için vasküler görüntüleme dikkatle değerlendirilmelidir. Objective: Fenestration is a vascular variation that begins with a common origin, then splits into two parallel luminal channels that rejoins distally. We aim to evalute the frequency of cerebral arterial fenestrations and their association with cerebral aneurysm by computed tomography (CT) angiography. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed cerebral CT angiography of patients obtained between January 2017 and December 2020. Patients older than 18 years-old, without known vascular disease and previous surgery or interventional treatment were included the study. The location of the fenestration and aneurysms were noted. Results: CT angiographies of 887 patients (mean age 54.8 years, range 18-63 years; 405 women and 482 men) were evaluated. 164 fenestrastions found in 152 patients for a detection rate of 17.1%. Anterior communicating artery fenestrations were the most common (51.2%), followed by vertebrobasilar system fenestration (28.7%). In our study, no significant relationship was found between fenestration and aneurysm, regardless of localization (p>0.05). However, in the coexistence of fenestration and aneurysm, these are commonly located at the same localization (p: 0.005). Conclusion: Cerebral artery fenestration is an uncommon and mostly affects the anterior communicating artery and vertebrobasilar system. Cerebral artery fenestrations could be associated with aneurysms at the fenestration site. Further attention should be paid to the coexistence of aneurysm once intracranial artery fenestration has been found. |
| 16. | Managerial Preparation and Process Management in a 3rd Stage Hospital had Became a Pandemic Hospital in the Fight Against the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Study From Turkey Enver İlhan, Özden Yıldırım Akan, Sema Aktolga, Ayşen Yalçınkaya, Mehmet Burak Öztop doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.92979 Pages 374 - 384 (492 accesses) Amaç: Pandemiye hazırlık ve süreç yönetiminde alınan tedbirler, yapılan düzenlemeler, acil olaylar karşısında verilen reaksiyonlar ve geliştirilen yeni stratejileri sunmak ve paylaşmaktır. Yöntem: Pandemiye hazırlık aşamasında, kurulan kurullar, kriz masası oluşturulması, alınan kararlar, hastane içinde yapılan, fiziki düzenlemeler, personel hazırlıkları, olası/kesin Covid-19 tanılı hastaların Covid -19 polikliği ve Acil Servis’ten itibaren yönetimi, Pandemi Servisleri ve Yoğun Bakımların yönetimi, hasta sevk ve kabulleri, acil gelişen problemlere karşı geliştirilen çözümler, sağlık çalışanının bulaştan korunması için alınan tedbirler, personel sağlık taramaları, sağlık çalışanına ve hastalara psiko-sosyal destek, poliklinikler, ameliyathanelerin yönetimi. Ek olarak Covid-19 hasta verilerinin hızlı bir şekilde yerel ve merkezi yönetim birimlerine ulaştırılması, PCR ve hızlı test uygulamaları, tüm alanlarda personel çalışma ve nöbet sistemleri, esnek çalışma sistemi, ve nihayetinde hastalarla ilgili sonuçları içeren veriler retrospektif olarak değerlendirildi. Bulgular: Covid-19 polikliniğine toplamda 5062 hasta başvurdu. 232’si olası/kesin Covid-19 tanısıyla tedavisi düzenlenerek ayaktan takibe alındı. 388 hasta hastaneye yatırıldı, Diğer yandan Acil servise başvuran olası/kesin Covid-19 tanılı hastaların 463 ü hastaneye yatırıldı. Bu hastalardan 169’u yoğun bakımlara yatırıldı. Toplam ve mekanik ventilasyon, solunum desteği ve yoğun bakım takibi gerektiren hastalarda mortalite hızı sırasıyla %11,3 ve %61,1 idi. 1982 hastane personelinden 38’inde bulaş görüldü. Personellerde mortalite görülmedi. Sonuç: Pandemi süreci aktif, değişken ve dinamik bir süreç olup kurumların her zaman bu tür pandemilere hazırlıklı olması ve hastanelerinin yönetsel tecrübelerini paylaşmaları, devam eden pandemi sürecinde ve yeni gelişebilecek salgın durumlarında hastanelerin yönetimlerinin strateji geliştirmesine yardımcı olacaktır. Ancak daha iyi sonuçlar için yeni yönetim süreçleri araştırılmalıdır. Objective: We aimed to present and share the measures taken in pandemic preparedness and management process; the regulations made, the reactions given to emergency events and the new developed strategies Methods: The pandemic preparation phase, hospital arrangements, physical arrangements, personnel planning, crisis desk establishment for the pandemic process,the management of the patients with suspected/definite Covid-19 diagnosis from the referral to Covid-19 outpatient clinic and Emergency Service, the management of Pandemic Services and Intensive Care Units 0, solutions for urgent problems, also precautions taken for possible contamination of healthcare workers and their health screenings, psychosocial support for healthcare workers and patients, planning’s for outpatient clinics, operating rooms. In addition rapid delivery of Covid-19 patients’ data to local and central government, PCR and rapid test applications, personnel work and shift systems in all areas, flexible working system, and finally, data including ex rates related to patients were evaluated retrospectively. Results: Five thousand sixty two patients applied to the Covid-19 polyclinic. For 232 of patients diagnosed with suspected/confirmed COVID-19, treatment was planned and followed-up as outpatients. Three hundred eighty-eight patients were hospitalized,. On the other and, 463 of the patients with a suspected/confirmed diagnosis of Covid-19 who admitted to the emergency service were hospitalized. One hundred sixty nine of inpatients were admitted to intensive care units. Totally the patients who require mechanical ventilation, respiratory support, and intensive care follow-up was found 11.3% and 61.1%respectively. 38 of total 198 hospital staff had infected with Covid-19. Diseases were not mortal. Conclusion: The pandemic approach is an active, variable and dynamic process, and institutions should always be prepared for such pandemics in addition sharing hospitals’ managerial experiences will help to administrations to develop strategies in the ongoing pandemic process and in emerging situations. However, new management processes should be investigated for better results. |
| 17. | Open Hart Surgery Experience of a High Volume Center During Pandemic Kemal Karaarslan, Ayşe Gül Kunt, Burçin Abud doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.26878 Pages 385 - 391 (349 accesses) Objective: The aim of the study is to report the results of open heart surgery performed during the pandemic. Methods: One hundred eighty-five symptomatic patients were operated under a median sternotomy with a cardiopulmonary bypass in our pandemic hospital. They were all outpatient and were COVID-negative and strict precautions were taken. Results: 185 patients were referred to cardiovascular surgery for several type of cardiac operation. All patients were symptomatic due to primary cardiac disease. In-hospital mortality rate was seven times higher in those with Covid-19 (22.2%) while the non Covid-19 patients had a rate of (3.4%) (p<0.0001). Conclusion: Cardiac surgery is inevitable in symptomatic patients and can be done even with the risk of transmission and death. The patient, cardiac surgeon, and healthcare team should be aware of the ongoing contamination time. |
| 18. | Prognostic Value of Dysnatremia in COVID-19 Disease Şeyda Kayhan Ömeroğlu, Mehmet Burak Öztop doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.47640 Pages 392 - 400 (504 accesses) Objective: The infection of Corona 2019 (COVID-19) had first diagnosed in December 2019 and evolved into a worldwide pandemic in March 2020. In Turkey first diagnose was announced in March 2020. Low costed and easily accessible laboratory parameters needed for predicting the prognosis of this disease as its outcome pattern vary greatly from patient to patient. There is promising data on predicting the outcomes with disnatremic results. Methods: In this study we retrospectively investigated all adults with the diagnosis of COVID-19 who attended to Turkan Ozilhan Hospital over a 3 months period. We evaluated the relation of dysnatremia (hyponatremia as <135 mmol/L or hypernatremia as >145 mmol/L) for need of intensive care unit (ICU) treatment, need of intubation for mechanic ventilatory support and inpatient mortality. Results: one thousand seventy tree patients with COVID-19 [53..9% males (793 patients) and 46.1% females (680 patients), were investigated for this study. Their median age was 53.9 years ranging betweent 19-94. The dysnatremic groups had significantly higher rates of need for ICU and intubation The need for ICU was 89 (21.5%) patients in normonatremic group but 38 (76%) patients in hypernatremic and 71 (64%) in hyponatremic patients (p<0.01 for each of them). The mortality rate was 5% in normonatremic patients but 50% in hypernatremic and 28% in hyponatremic patients (p<0.01 for each of them). Conclusion: In this study we aimed to draw attention to the importance of abnormal sodium levels as a predictive marker in COVID-19. In small town hospitals the physicians should be aware of the risks of disnatremic patients with COVID-19 and take precautions while treating them. |
| 19. | Analysis of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in 281 Cases of Hospitalized Covid 19 Patients, Single-Center Study Gözde Derviş Hakim, Şükran Köse, Pınar Şamlıoğlu, Cengiz Ceylan, Mehmet Can Ugur, Rıfat Somay, Pelin Adar, Ayfer Çolak doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.73603 Pages 401 - 408 (421 accesses) Objective: Although Covid-19 which has been identified as the disease caused by SARS COV-2 virus mainly affects the respiratory tract, it was observed that many systems were affected. The gastrointestinal system is one of the main systems involved. The aim of this manuscript was to perform epidemiological, virological, and clinical analysis of 59 Covid 19-positive patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. Method: Covid-19 diagnosed patients have been started to be admitted since March, 20, 2020. Epidemiological, demographical, clinical findings, laboratory analyses as well as hospitalization periods and disease progression of the patients presenting gastrointestinal system (GIS) symptoms admitted between March, 31, 2020 and August, 1, 2020. Results: Totally 710 Covid 19-positive patients hospitalized were screened. Among these patients, those with incomplete medical history and deficient data were excluded. The analysis of 281 patients admitted due to Covid-19 diagnosis with complete data since admission revealed that 59 patients presented GIS symptoms at admission. The aforesaid patients were compared with 222 patients admitted due to Covid-19 without GIS symptoms within the same period. GIS symptoms were detected on 59 (59/281) (20.99%) patients admitted due to Covid-19. Detailed review of these patients revealed that 18 (18/59) (30.50%) patients had nausea-vomiting, 10 (10/59) (16.95%) patients had abdominal pain, and 31 (31/59) (52.55%) patients had GIS bleeding. It was observed that vomiting was added into the clinical presentation in 7 of 18 patients. Although there is not any diarrhea symptom alone, total number of cases with diarrhea+abdominal pain, diarrhea+nausea-vomiting, diarrhea+nausea-vomiting+abdominal pain was 17 (17/59) (28.81%) of 59 patients. Conclusion: According to the results of this study, we have found 20.99% gi symptoms in the hospitalizated patients due to Covid 19. Although GIS symptoms are not associated with disease severity, they are important for the identification and spread of the disease, along with respiratory symptoms. |
| CASE REPORT | |
| 20. | Posttransplantation Vesicoureteral Reflux in Renal Grafts and Their Outcomes in Pediatric Transplantation: Should We Be Afraid ? Demet Alaygut, Eren Soyaltın, Elif Perihan Öncel, İsmail Sert, Cem Tuğmen, Tunç Özdemir, Önder Yavaşcan, Fatma Mutlubaş, Caner Alparslan, Belde Kasap-Demir doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.39358 Pages 409 - 415 (471 accesses) Amaç: Greft böbreğinde vezikoüreteral reflü (VUR) olan dört pediatrik olgunun demografik, transplantasyon öncesi ve transplantasyon özellikleri ve tedavi sonrası sonuçları tartışıldı. Yöntem: 2008-2016 yılları arasında Tepecik Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi’nde böbrek nakli yapılan ve rekürren idrar yolu enfeksiyonu nedeniyle voiding sistouretrografiyi (VCUG) ile graft böbrekte VUR tespit edilen dört hastanın transplantasyon yaşı, primer tanısı, nativ böbreklerde pre transplantasyon VUR, mesane disfonksiyonu öyküsü, mesane kapasitesi, ürodinamik çalışmaların sonuçları, donör ve özellikleri, indüksiyon tedavileri ve devam eden immünosüpresif tedaviler, akut rejeksiyon epizotları, CMV ve BK enfeksiyonları, VUR derecesi, DMSA sonuçları, tedavi şekli ve sonuçları ve böbrek greft fonksiyonları değerlendirildi. Bulgular: Dört vakanın tümü kızdı. Ortalama nakil yaşı 8.7 (5-16) yıl idi. Greft böbreklerinden bir tanesi dışında hepsinde (4. derece) VUR tespit edildi. DMSA, düşük dereceli VUR olan bir olgu dışında çoklu skar odakları içeriyordu. Olgular öncelikle endoskopik olarak ve daha sonra açık cerrahi ile tedavi edildi. Bir vakada kendiliğinden iyileşme meydana geldi. Hiçbir olguda greft fonksiyon bozukluğu gözlenmedi. Sonuç: VUR, nakil sonrası tekrarlayan idrar yolu enfeksiyonlarında önemli bir risk faktörüdür. VUR varlığında hasta için özel bir değerlendirme yapılmalıdır. Konservatif ve cerrahi tedaviler birlikte uygulanmalıdır. VUR’un mesane kapasitesi arttırıcı tedaviler ve profilaksi ile kendiliğinden gerileyebileceği unutulmamalıdır. Objective: Demographical, pre-transplantation and post-transplantation features and post-treatment results of four pediatric cases, who had vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in the graft kidney, were discussed. Methods: Transplantation age, primary diagnosis, VUR to pretransplantation in native kidneys, history of bladder dysfunction, bladder capacity, results of urodynamic studies, donor and its features, induction treatments and ongoing immunosuppressive treatments, acute rejection episodes, CMV and BK infections, VUR grade in the renal graft, DMSA results, treatment type and its outcomes, and the renal graft functions of four patients who underwent kidney transplantation at Tepecik Training and Research Hospital between 2008 and 2016 and for whom VUR was determined via voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) due to recurrent urinary tract infections, were evaluated. Results: All of four cases were female. Their mean transplantation age was 8.7 years (5-16). High grade (Grade 4) VUR was determined in the graft kidney in all but one. DMSA included multiple scar foci apart from one case having low grade VUR. Cases were primarily treated endoscopically and then by open surgery. Spontaneous recovery occurred in one case. Graft dysfunction was not observed in any of the cases. Conclusion: VUR is an important risk factor in recurrent urinary tract infections after post-transplantation. A special assessment should be done for the patient in the presence of VUR and conservative and surgical treatments should be executed together. It should be remembered that VUR can be spontaneously regressed by the bladder capacity increasing treatments and prophylaxis. |
| 21. | Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome During Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment Sila Atamyildiz, Eda Ataseven, Cenk Eraslan, Mehmet Kantar doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.36037 Pages 416 - 430 (511 accesses) Posterior reversible ensefalopati sendromu (PRES), akut başlangıçlı baş ağrısı, mental durum bozukluğu, görme bozukluğu, bulantı, kusma, nöbet ve hipertansiyon ile karakterize klinik ve radyolojik olarak tanımlanmış bir sendromdur. PRES erken farkedildiğinde geri dönüşümü olan bir durumdur. Ancak bazı vakalarda kalıcı nörolojik hasara hatta ölüme bile yol açabilir. Burada, ALL indüksiyon tedavisi sırasında PRES gelişen iki olguyu literatür ile beraber değerlendirdik, ALL tedavisi sırasında karşılaşabileceğimiz bu önemli duruma dikkat çekmeyi ve farkındalığı arttırmayı hedefledik. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a clinical and radiological syndrome, characterized by acute onset of headache, altered mental status, visual impairment, nausea, vomiting, seizure, and hypertension. PRES is a reversible condition if it is recognized early, but neurological damage or even death may occur. Herein, we present two cases of ALL who developed PRES during their induction therapy and a literature review of PRES. |
| 22. | Anesthetic management in Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis: Case Report Muhammed Celil Aslan, Cengiz Sahutoglu, Canan Bor doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.79664 Pages 421 - 424 (865 accesses) Neuronal Ceroid Lipofucinosis is the most common neurodegenerative disease of childhood. The most common findings are neurological developmental disorders and cardiac conduction anomalies. Anesthesia management is specific in terms of hypothermia and bradycardia that may develop during surgery. The presence of muscle involvement in severe cases also requires caution in drug selection. In this case, anesthesia management in a late-infant type NCL patient who underwent phimosis operation is presented. Nöronal Seroid Lipofusinozis çocukluk döneminin en sık görülen nörodejeneratif hastalığıdır. En sık bulguları nörolojik gelişim bozuklukları ve kardiyak iletim anomalileridir. Anestezi yönetimi ameliyat sırasında gelişebilecek hipotermi ve bradikardi açısından özelliklidir. Ağır olgularda kas etkilenimi olması da ilaç seçiminde dikkatli olmayı gerektirir. Bu olguda fimozis operasyonu uygulanan geç-infant tip NSL hastasında anestezi yönetimi sunulmuştur. |
| 23. | A Case with Holt-Oram Syndrome Tülay Demircan, Özgür Kızılca, Nuh Yılmaz, Mustafa Kır, Nurettin Ünal doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.73644 Pages 425 - 427 (807 accesses) Holt-Oram sendromu üst ekstremite anomalileri ve doğumsal kalp hastalıkları ile karakterize, otozomal domiant katılımlı bir sendromdur. Doğumsal kalp defektlerinden en sık atriyal septal defekt (ASD) eşlik eder. Beş yaşında kız olguya; 2 yaşında iken ASD, baş parmağının trifalankslı olması ve babasında da ASD ve el anomalisi olması nedeniyle Holt-Oram sendromu tanısı konuldu. İlk planda ASD’nin transkateter kapatılması planlandı fakat transözafagiyal ekokardiyografi ile rimlerinin uygun olmadığına karar verilerek ASD’si cerrahi olarak kapatıldı. Bu makale, üst ekstremite anomalisi olan hastalarda doğumsal kalp defektlerininde eşlik edebileceğinin anımsanması ve ender görülen bir sendrom olan Holt-Oram sendromunun akla getirilmesi amacı ile sunuldu. Holt-Oram syndrome is an autosomal domiant- associated syndrome characterized by upper extremity anomalies and congenital heart diseases. Of the congenital heart defects, atrial septal defect (ASD) is most frequently accompanied. A five-year-old girl; When she was 2 years old, she was diagnosed with Holt-Oram syndrome because of her ASD, her thumb with triphalanx, and her father with ASD and hand anomalies. Transcatheter closure of ASD was planned in the first plan, but it was decided by transesophageal echocardiography that the rims were inappropriate, and ASD was closed surgically. This article is presented with the aim of remembering that congenital heart defects may accompany patients with upper extremity anomaly and to think of Holt-Oram syndrome which is a rare syndrome. |
| 24. | A Rare Case Presenting with “Bloody Tears”: Idiopathic Unilateral Hemolacria Gizem Doğan, Secil Arslansoyu Çamlar, Kayi Eliacik, Emre Ayintap, Mehmet Helvacı doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.52297 Pages 428 - 431 (675 accesses) Hemolakri, kanlı gözyaşı olarak da bilinen ve gözlerden kan gelmesi olarak tanımlanan tıbbi bir durumdur. Hemolakri nedenleri arasında göz enfeksiyonları, travma, kanama bozuklukları, göz ve lakrimal kanal maligniteleri, hipertansiyon, hipertiroidizm, retrograd epistaksis ve endometriozis bildirilmiştir. Altta yatan bir neden bulunamadığında, bu durum idiyopatik hemolakri olarak tanımlanır. İdiyopatik hemolakri, iyi huylu ve kendi kendini sınırlayan bir durumdur. Burada kanlı gözyaşları olan 15 yaşındaki ergen bir çocuğu sunuyoruz. Sağ göz çevresinde ağrı ve sağ baş ağrısı vardı. Gözlerde akıntı, kızarıklık, bulanık görme, burunda kanama gibi başka bir bulgusu yoktu. Fizik muayenede; sağ punktumdan başlayan kırmızı sıvısı vardı. Görsel muayenede tam görme kapasitesi, doğal bilateral ön segmentler, açık fundus, doğal ve yumuşak retina, yabancı cisim veya enfeksiyon bulgusu yoktu. Hastanın tanısal incelemelerinde etiyolojik bir etken bulunamadı. Hasta idiyopatik tek taraflı hemolakri tanısıyla takibi sırasında hemolakri haftada iki kez meydana geldi ve birkaç gün içinde sınırlı kaldı. Hemolacria is known as bloody tears and described as blood coming from the eyes. Eye infections, trauma, bleeding disorders, eye and lacrimal canal malignancies, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, retrograde epistaxis and endometriosis have been reported among the causes of hemolacria. When no underlying cause can be found, this condition is defined as idiopathic hemolacri and is knokn as a benign and self-limiting condition. In this case report we present a 15-year-old an adolescent boy with bloody tears. He had pain around the right eye and headache on the right side of head. He had no other findings as discharge in the eyes, redness, blurred vision, or bleeding in the nose. On physical examination; we observed red fluid starting from the right punctum. Visual examination revealed complete visual capacity, natural bilateral anterior segments, clear fundus, natural and soft retina, and no foreign body or infection findings. Etiological factor was not found in the diagnostic investigations of the patient. The patient was followed with the diagnosis of idiopathic unilateral hemolacria. The hemolacria occurred twice a week and limited itself within several days. Hemolacria is a rare condition and should be evaluated together with pediatricians and ophthalmologists within a multidisciplinary approach. |
| 25. | Iatrogenic Right Subclavian Artery Giant Pseudoaneurysm in a 1-Year Old Case Ömer Faruk Gülaştı, Eyüp Halit Yardımcı doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.64325 Pages 432 - 435 (361 accesses) Santral venöz girişim çocuk yoğun bakım ünitelerinde sık olarak yapılmaktadır. Bu girişimlere bağlı hayatı tehdit edici komplikasyonlar nadiren meydana gelmektedir. Doğumundan itibaren yoğun bakım ünitesinde takip edilen 1 yaşındaki olguda, sağ subklavyen kateter girişiminden yaklaşık 1 ay sonra psödoanevrizma tespit edilmiştir. Sağ brakial pleksus bası bulguları izlenen, sağ kol arteriyel akımda azalma ve vena kava süperior sendromu bulguları gelişmeye başlayan hastaya sağ supraklavikuler ve median sternotomi kombinasyonu modifiye ‘trapdoor’ kesi ile cerrahi uygulandı. Central venous punctures are performed frequently in pediatric intensive care units, but life threatening complications are rare due to these. A pseudoaneurysm was observed after 1 month following right subclavian puncture, in a 1-year old case, who has been followed at intensive care units since birth. Surgery was performed by modified ‘trapdoor’ incision as a combination of right supraclavicular and median sternotomy incisions to the case; suffering from right brachial plexus compression symptoms, diminished right arm arterial flow, and vena cava superior syndrome symptoms. |
| LETTER TO THE EDITOR | |
| 26. | COVID-19 and Low Uric Acid Levels Mesut Aydın, Alev Gül, Yaren Dirik, Ahmet Cumhur Dülger, Harun Egemen Tolunay doi: 10.5222/terh.2021.03753 Pages 436 - 438 (404 accesses) Abstract | |
| 27. | Author Indeks Page E1 (263 accesses) Abstract | |
| 28. | Subject Index Page E2 (247 accesses) Abstract | |